Planning for retirement is a crucial step in securing your financial future. With the increasing uncertainty surrounding government-funded programs, private retirement plans like IRAs (Individual Retirement Accounts) and 401(k)s have become more popular. In this article, we will explore the differences between private retirement plans and Social Security, helping you make informed decisions about your retirement savings strategy.
What is a Private Retirement Plan?
A private retirement plan is a savings account that individuals can set up independently or through their employer to save for retirement. These plans offer various tax advantages, making them an attractive option for long-term financial growth. The two most common types of private retirement plans in the United States are the IRA and the 401(k).
Understanding IRAs (Individual Retirement Accounts)
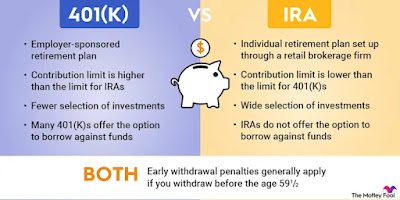
An IRA is a personal savings plan that offers tax advantages for retirement savings. There are several types of IRAs, including Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs, each with its own set of rules and benefits.
Traditional IRA: Contributions to a Traditional IRA may be tax-deductible, and the investment earnings grow tax-deferred until you withdraw the funds during retirement. Withdrawals are taxed as regular income.
Roth IRA: Unlike a Traditional IRA, contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars, meaning you pay taxes upfront. However, the earnings grow tax-free, and qualified withdrawals during retirement are also tax-free.
Understanding 401(k) Plans
A 401(k) is an employer-sponsored retirement plan that allows employees to contribute a portion of their paycheck to a retirement account. Like IRAs, 401(k)s offer tax advantages, but there are some key differences.
Employer Matching: One of the significant benefits of a 401(k) is that many employers offer a matching contribution, effectively giving you free money toward your retirement.
Contribution Limits: 401(k) plans typically have higher contribution limits compared to IRAs, allowing you to save more aggressively.
Tax Benefits: Contributions to a 401(k) are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income for the year. However, like a Traditional IRA, withdrawals are taxed as regular income.
How Social Security Fits In
Social Security is a government-funded program designed to provide financial support during retirement. Unlike private retirement plans, Social Security is funded through payroll taxes and is not based on individual contributions. Instead, it provides a guaranteed income based on your earnings history and the age at which you start claiming benefits.
While Social Security is a valuable resource, it is generally not sufficient to cover all your retirement needs. This is why many financial advisors recommend supplementing Social Security with private retirement plans like IRAs and 401(k)s.
The Importance of Diversifying Your Retirement Savings
Relying solely on Social Security for retirement income is risky due to the program's potential future challenges. By diversifying your retirement savings across multiple accounts, such as a 401(k), IRA, and Social Security, you can create a more robust financial safety net. This diversification allows you to maximize your tax advantages, take advantage of employer contributions, and ensure a more secure retirement.
Conclusion
Planning for retirement requires careful consideration of various factors, including your income, expenses, and long-term financial goals. By understanding the differences between private retirement plans like IRAs and 401(k)s and how they complement Social Security, you can create a well-rounded strategy that ensures a comfortable and secure retirement.
.jfif)
.png)




No comments:
Post a Comment